Are you tired of seeing your furry friend struggle with digestive issues, lackluster coats, or low energy levels? 🐾 The solution might be simpler than you think – a raw diet. But before you make the switch, it’s crucial to understand both sides of the coin.
Raw diets for pets have gained popularity in recent years, with proponents claiming benefits ranging from improved digestion to shinier coats. However, this feeding method isn’t without controversy. Veterinarians and pet nutrition experts are divided on the topic, with some praising its potential benefits and others warning of possible risks.

In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of raw pet diets. We’ll explore the potential pros and cons, share expert opinions, and provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision for your furry companion. Whether you’re considering a raw diet or simply curious about alternative feeding options, read on to discover everything you need to know about this controversial yet intriguing approach to pet nutrition.
Understanding Raw Diets for Pets
Definition and components of raw diets
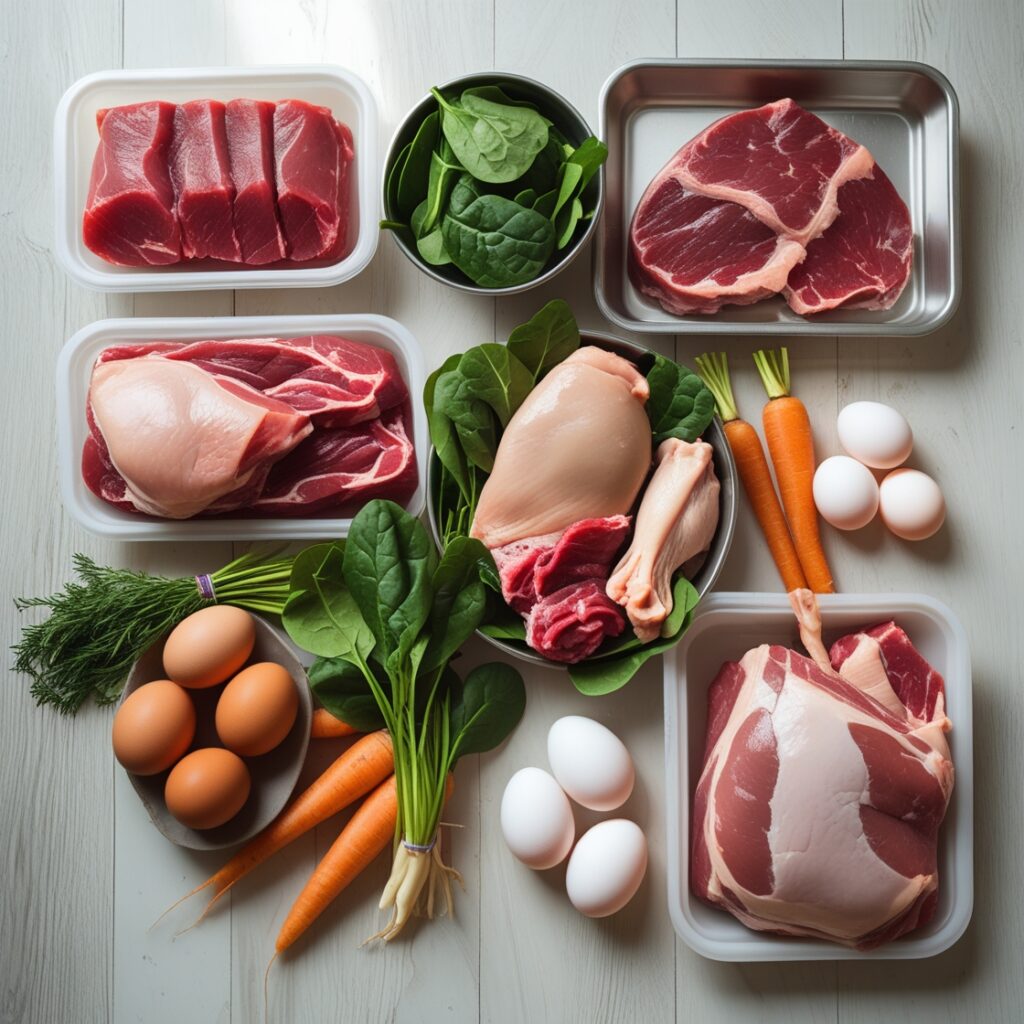
Raw diets for pets typically consist of uncooked animal products, including:
- Muscle meat
- Organ meat (e.g., liver, kidneys)
- Raw bones
- Raw eggs
- Fruits and vegetables (in some diets)
These diets aim to mimic what animals would eat in the wild, focusing on natural, unprocessed ingredients. Here’s a breakdown of common components:
| Component | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle meat | Primary protein source | Chicken, beef, lamb |
| Organ meat | Vitamins and minerals | Liver, heart, kidneys |
| Raw bones | Calcium and dental health | Chicken necks, beef ribs |
| Fruits/Vegetables | Fiber and nutrients | Carrots, apples, spinach |
Types of raw diets (BARF, Prey Model, etc.)
Two main types of raw diets are popular among pet owners:
- BARF (Biologically Appropriate Raw Food):
- Includes meat, bones, organs, and vegetables
- Aims to balance nutrients similar to ancestral diets
- Prey Model Raw (PMR):
- Focuses on whole prey animals
- Excludes plant matter
- Mimics what wild carnivores would eat
Popularity and recent trends
Raw diets have gained significant traction in recent years:
- Increased awareness of pet nutrition
- Social media influence and celebrity endorsements
- Growing availability of commercial raw food products
Recent trends include:
- Freeze-dried raw options for convenience
- Hybrid diets combining raw and traditional kibble
- Customized raw meal plans tailored to individual pets
As pet owners seek more natural alternatives, raw diets continue to evolve and attract attention in the pet food industry.
Potential Benefits of Raw Diets
Improved dental health
One of the most notable benefits of a raw diet for pets is the potential improvement in dental health. Raw meaty bones and tough tissues act as natural toothbrushes, helping to:
- Remove plaque and tartar buildup
- Strengthen jaw muscles
- Promote healthy gum tissue
| Dental Benefit | How Raw Diet Helps |
|---|---|
| Plaque reduction | Chewing action scrapes teeth clean |
| Tartar prevention | Enzyme-rich raw food discourages buildup |
| Gum health | Increased blood flow from chewing |
Shinier coat and healthier skin
Raw diets often lead to a noticeable improvement in coat quality and skin health. This is primarily due to:
- Higher levels of essential fatty acids
- Improved nutrient absorption
- Reduced inflammatory responses
Pets on raw diets frequently exhibit glossier fur, less shedding, and fewer skin issues.
Increased energy levels
Many pet owners report a boost in their pets’ energy and vitality after switching to a raw diet. This may be attributed to:
- More bioavailable nutrients
- Improved metabolism
- Better overall health
Better digestion and smaller stools
Raw diets can significantly impact a pet’s digestive system, often resulting in:
- More efficient nutrient absorption
- Reduced instances of gastrointestinal issues
- Smaller, firmer stools with less odor
This improved digestion is largely due to the absence of fillers and artificial additives found in many processed pet foods. As we explore these potential benefits, it’s important to also consider the possible drawbacks and risks associated with raw diets, which we’ll discuss in the next section.

Possible Drawbacks and Risks
Nutritional imbalances
Raw diets can lead to nutritional imbalances if not carefully formulated. Many homemade raw diets lack essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals necessary for a pet’s overall health. This can result in deficiencies or excesses that may cause health problems over time.
| Nutrient | Potential Issue |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Deficiency can lead to weak bones |
| Phosphorus | Excess can cause kidney problems |
| Vitamin A | Toxicity can occur with overconsumption |
| Taurine | Deficiency can cause heart issues in cats |
Bacterial contamination
One of the most significant risks associated with raw diets is bacterial contamination. Raw meat can harbor harmful pathogens such as:
- Salmonella
- E. coli
- Listeria
- Campylobacter
These bacteria can cause severe gastrointestinal issues in pets and pose a risk to human health as well.
Choking hazards and dental injuries
Raw diets often include bones, which can present choking hazards or cause dental injuries. Pets may:
- Choke on small bone fragments
- Suffer from broken teeth when chewing on hard bones
- Experience internal injuries from sharp bone splinters
Higher cost and preparation time
Raw diets typically come with a higher price tag compared to commercial pet foods. Additionally, they require more time and effort to prepare, including:
- Sourcing high-quality ingredients
- Proper storage and handling of raw meat
- Daily meal preparation and portioning
Potential for human exposure to pathogens
Handling raw meat increases the risk of spreading harmful bacteria to humans. This is especially concerning for households with:
- Young children
- Elderly individuals
- People with compromised immune systems
Proper hygiene and food safety practices are crucial when preparing raw diets to minimize this risk.
Veterinary Perspectives on Raw Diets
Arguments in favor of raw feeding
Some veterinarians advocate for raw diets, citing potential benefits:
- Improved dental health
- Better digestion and nutrient absorption
- Enhanced coat quality and skin health
- Increased energy levels
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Dental health | Raw bones act as natural toothbrushes |
| Digestion | Enzymes in raw food aid nutrient absorption |
| Coat & skin | Higher quality proteins improve fur and skin |
| Energy | Balanced, species-appropriate nutrition boosts vitality |
Concerns raised by veterinary professionals
Many vets express reservations about raw diets:
- Bacterial contamination risks (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli)
- Potential for nutritional imbalances
- Choking hazards from bones
- Increased risk of parasitic infections
Varying opinions within the veterinary community
The veterinary field is divided on raw feeding:
- Pro-raw vets often emphasize evolutionary appropriateness
- Anti-raw vets focus on safety and balanced nutrition
- Some recommend partial raw diets as a compromise
This diversity of opinions reflects the complexity of pet nutrition and the need for ongoing research. Pet owners should consult with their veterinarians to make informed decisions based on their individual pets’ needs and health status.
Considerations Before Switching to a Raw Diet
Pet’s age, health status, and breed
Before transitioning your pet to a raw diet, it’s crucial to consider their individual characteristics. Different factors can influence how well a pet may adapt to and benefit from a raw diet:
- Age: Puppies and kittens have different nutritional needs compared to adult or senior pets.
- Health status: Pets with certain health conditions may require specialized diets.
- Breed: Some breeds may have specific dietary requirements or sensitivities.
| Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Age | Puppies/kittens need balanced nutrition for growth |
| Senior pets may have reduced digestive capabilities | |
| Health | Pets with compromised immune systems may be at higher risk |
| Certain conditions (e.g., pancreatitis) may contraindicate raw diets | |
| Breed | Some breeds are prone to specific health issues affected by diet |
Owner’s ability to handle raw food safely
Preparing raw diets requires strict hygiene practices to prevent foodborne illnesses:
- Proper storage of raw ingredients
- Thorough cleaning of preparation surfaces and utensils
- Safe handling and disposal of raw meat products
- Regular sanitization of food bowls
Consulting with a veterinary nutritionist
A veterinary nutritionist can provide valuable guidance:
- Assess your pet’s specific nutritional needs
- Design a balanced raw diet plan
- Recommend appropriate supplements if necessary
- Monitor your pet’s health during the transition
Gradual transition process
Switching to a raw diet should be done gradually to avoid digestive upset:
- Start by introducing small amounts of raw food
- Gradually increase the proportion of raw food over 1-2 weeks
- Monitor your pet’s response and adjust as needed
- Be prepared to slow down or pause the transition if issues arise
Now that you understand the key considerations, let’s explore some alternatives to full raw diets that may offer similar benefits with potentially fewer risks.
Alternatives to Full Raw Diets
Partial raw feeding
Partial raw feeding offers a balanced approach for pet owners interested in raw diets but hesitant to commit fully. This method involves combining raw food with traditional kibble or wet food, allowing pets to benefit from both nutritional profiles.
- Advantages of partial raw feeding:
- Gradual transition
- Cost-effective
- Nutritional balance
- Flexibility
| Meal Component | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Raw food | 25-50% |
| Kibble/Wet food | 50-75% |
Freeze-dried or dehydrated raw options
For those seeking convenience without compromising on raw nutrition, freeze-dried or dehydrated raw options present an excellent alternative. These products undergo minimal processing, preserving nutrients while eliminating pathogens.
Benefits:
- Extended shelf life
- Easy storage and portability
- Reduced risk of bacterial contamination
- Convenient rehydration process
High-quality commercial pet foods
High-quality commercial pet foods provide a safe and nutritionally complete alternative to raw diets. These products are formulated by veterinary nutritionists and undergo rigorous testing to ensure balanced nutrition.
- Key features to look for:
- Named meat sources as primary ingredients
- No artificial preservatives or colors
- Added vitamins and minerals
- AAFCO statement of nutritional adequacy
Now that we’ve explored alternatives to full raw diets, it’s important to consider your pet’s individual needs and consult with a veterinarian before making any significant dietary changes.
Raw diets for pets have gained popularity among pet owners seeking to provide their furry companions with a more natural and nutritious diet. While potential benefits include improved digestion, healthier skin and coat, and increased energy levels, it’s crucial to consider the risks associated with raw feeding, such as bacterial contamination and nutritional imbalances. Veterinary opinions on raw diets remain divided, with some professionals advocating for their benefits and others expressing concerns about potential health hazards.
Before making the switch to a raw diet, pet owners should carefully weigh the pros and cons, consult with their veterinarian, and consider their pet’s individual needs. For those interested in incorporating raw elements into their pet’s diet without fully committing to a raw feeding regimen, alternatives such as partially cooked diets or high-quality commercial foods with raw components may offer a balanced compromise. Ultimately, the decision to feed a raw diet should be made with careful consideration and professional guidance to ensure the best possible outcome for your beloved pet.



